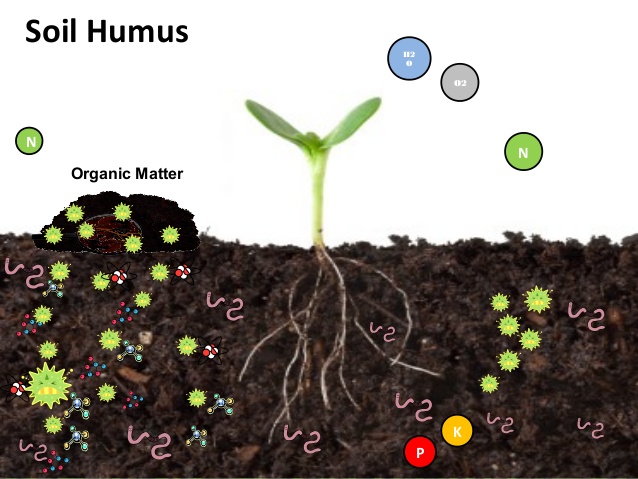
Soil humus is an important component of healthy soil. It is the organic matter that forms when plant and animal matter decomposes in the soil. Humus is made up of a mixture of decomposed plant material, such as leaves, twigs, and roots, and microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi.
Humus is essential for the health of plants and the soil as it plays several vital roles. For example, it helps to improve the structure of the soil, making it more porous and easier for roots to penetrate. This improves the soil’s water-holding capacity, making it more resistant to drought.
Humus also helps to improve the nutrient content of the soil. As organic matter breaks down, it releases nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for plant growth. Additionally, humus can act as a sponge, holding onto nutrients and releasing them slowly to the plants as they need it.
Humus also plays a critical role in soil biodiversity. By providing a food source for microorganisms, it encourages a healthy population of bacteria, fungi, and other organisms that are essential for soil health. These organisms help to break down organic matter, improve nutrient cycling, and protect plants from pests and diseases.
Humus is also beneficial for soil carbon sequestration, which is the process of capturing and storing carbon in the soil. Organic matter, like humus, is rich in carbon, so when it is added to the soil, it helps to sequester carbon and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Humus can be increased in soil through methods such as composting, adding organic matter and by using cover crops. However, it takes time for humus to build up in the soil, so it’s important to be patient and maintain consistent practices.
In summary, Soil humus is an important component of healthy soil, It is the organic matter that forms when plant and animal matter decompose in the soil. It plays several vital roles such as improving the structure of the soil, improving the nutrient content, promoting soil biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. It can be increased in soil through methods such as composting, adding organic matter and by using cover crops.
